1007 分配宝藏
1007
分配宝藏
题目描述:
船长拥有\(\infty\)宝藏,要求分给士兵们,确定好分配方案后士兵们会投票,如果大于等于半数的人(包括船长)对分配认可,那么可按此分配;否则,船长被处死,第一继承人上位。问如何分配船长能在分出最少的情况下活下来。
解题思路:(\(n\)
表示士兵的个数)
n = 1 :
船长的1票已经过半,该士兵可给可不给,因为要求分出最少,所以给 0 。
n = 2 :
第一顺位一定投反对,因为如果Ta成为船长就可以拥有所有宝藏;因为赞同票需要过半,对于第二顺位,如果这一票Ta不投赞成,那么在下一轮Ta无法获得宝藏,所以只需给Ta
1 个宝藏,Ta就会获得比下一轮多的宝藏,Ta就会投赞同。
n = 3 :
第一顺位一定投反对,因为如果Ta成为船长就可以拥有所有宝藏;第二顺位如果到下一轮将获得
0 宝藏,所以只需给Ta
1个宝藏,Ta就会投赞同;因为包括船长自己票数过半,所以第三顺位可给可不给,
因为要求给出最少,所以给0。
n = 4:第一顺位一定投反对,因为如果Ta成为船长就可以拥有所有宝藏;第二顺位如果到下一轮将获得
0 宝藏,所以只需给Ta 1个宝藏,Ta就会投赞同;第三顺位如果到下一轮将获得 1
宝藏,第四顺位如果到下一轮将获得 0
宝藏,显然拉拢第四顺位所需宝藏更少,所给第三顺位 0 宝藏, 第四顺位 1
宝藏。
……
以此类推,可列出给出结果如下:
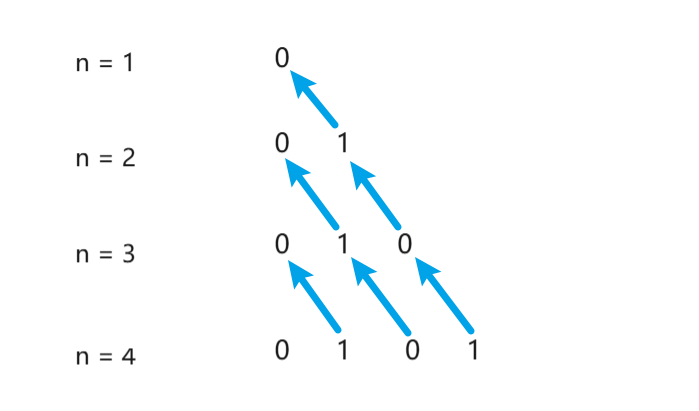
如此观察可知:奇数位分出 0 宝藏, 偶数位分出 1 宝藏
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
int solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
if(n == 1) return 0;
return (2 + n / 2 * 2) * (n / 2) / 2 % mod;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
cout << solve() << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
1005 航线
1005
航线
思路1:
对于每个格子,不仅有“距离”的消耗,还有转向的消耗,所以我们可以直接将每个格子拆成四个格子
那么图形的转换如下图:
其中灰色的线上标的数字是转向所需要的消耗,每一“块”中灰色线的消耗相同,
即数组 \(t[i][j]\);粉色的线是“距离”所需的消耗,即数组
\(g[i][j]\)

给每个节点一个编号,建图,套用Dijkstral即可
思路2:
利用\(Dijkstral\),对于priority中存储的是
1
2
3
4
| struct node
{
int time, x, y, dir;
};
|
分别表示到该节点消耗的时间,节点的 \(x\), \(y\) 坐标,以及该节点的方向
用 \(dist[x][y][dir]\) 存储到 \((x, y)\) 方向为\(dir\)的节点的最短时间
if(time != dist[x][y][dir]) continue用来防止重复遍历节点
时间转移有两种方式:
方式1:
先处理移动,再处理转向
- 即先判断,如果可以沿着当前方向走,且下个节点的 \(dist[x2][y2][i]\) 大于当前节点的 \(dist[x1][x1][i] + g[x1][y1]\)
,那么就将该方向的下一个节点\(dist\)
更新,并加入队列
1
2
3
4
5
| if (dist[nx][ny][dir] > time + g[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny][dir] = time + g[nx][ny];
q.push({dist[nx][ny][dir], nx, ny, dir});
}
|
- 再判断,在当前节点,如果方向 \(i\)
和原方向 \(dir\) 不同,且 \(dist[x][y][i] > dist[x][y][dir] +
t[x][y]\) 就更新为加上转向的消耗
1
2
3
4
5
| if (dist[x][y][i] > time + t[x][y])
{
dist[x][y][i] = time + t[x][y];
q.push({dist[x][y][i], x, y, i});
}
|
结束时返回要求的节点和方向即可
完整实现代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int dx[] = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy[] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
struct node
{
int time, x, y, dir;
bool operator<(const node& other) const
{
return time > other.time;
}
};
int solve()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> g(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1)), t(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> g[i][j];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> t[i][j];
priority_queue<node> q;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dist(n + 1, vector<vector<int>>(m + 1, vector<int>(4, 1e18)));
q.push({g[1][1], 1, 1, 0});
dist[1][1][0] = g[1][1];
while(q.size())
{
node tp = q.top();
q.pop();
int time = tp.time, x = tp.x, y = tp.y, dir = tp.dir;
if(time != dist[x][y][dir]) continue;
int nx = x + dx[dir], ny = y + dy[dir];
if (nx >= 1 && nx <= n && ny >= 1 && ny <= m)
{
if (dist[nx][ny][dir] > time + g[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny][dir] = time + g[nx][ny];
q.push({dist[nx][ny][dir], nx, ny, dir});
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if (i == dir) continue;
if (dist[x][y][i] > time + t[x][y])
{
dist[x][y][i] = time + t[x][y];
q.push({dist[x][y][i], x, y, i});
}
}
}
if(dist[n][m][1] != 1e18) return dist[n][m][1];
return -1;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
cout << solve() << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
方式2:
转向和移动一起处理
直接遍历某个节点的四个方向,如果可以走
- 如果新的节点的地理位置可以以原方向走到,那么就不需要加上转向的消耗
- 如果新的节点需要转向才能走到,那么请加上原节点的转向消耗
在判断更新之后的是否更小,更小就更新
1
2
3
4
5
| if(newtime < dist[a][b][i])
{
dist[a][b][i] = newtime;
q.push({newtime, a, b, i});
}
|
在结束时,因为只有当能走到下一个节点时,上一个节点才有可能转向。所以对于最后一个节点
\((n,
m)\),按照上面的逻辑它是无法判断是否转向更优的,需要单独判断
1
2
3
4
5
6
| int ans = 1e18;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if(i != 1) ans = min(ans, dist[n][m][i] + t[n][m]);
else ans = min(ans, dist[n][m][i]);
}
|
完整代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int dx[] = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy[] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
struct node
{
int time, x, y, dir;
bool operator<(const node& other) const
{
return time > other.time;
}
};
int solve()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> g(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1)), t(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> g[i][j];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> t[i][j];
priority_queue<node> q;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dist(n + 1, vector<vector<int>>(m + 1, vector<int>(4, 1e18)));
q.push({g[1][1], 1, 1, 0});
dist[1][1][0] = g[1][1];
while(q.size())
{
node tp = q.top();
q.pop();
int time = tp.time, x = tp.x, y = tp.y, dir = tp.dir;
if(time != dist[x][y][dir]) continue;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if(a >= 1 && a <= n && b >= 1 && b <= m)
{
int turn = 0;
if(dir != i) turn += t[x][y];
int newtime = turn + g[a][b] + time;
if(newtime < dist[a][b][i])
{
dist[a][b][i] = newtime;
q.push({newtime, a, b, i});
}
}
}
}
int ans = 1e18;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if(i != 1) ans = min(ans, dist[n][m][i] + t[n][m]);
else ans = min(ans, dist[n][m][i]);
}
if(ans != 1e18) return ans;
return -1;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
cout << solve() << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|













